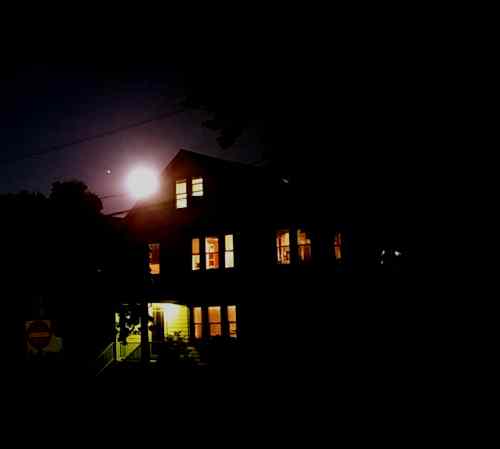
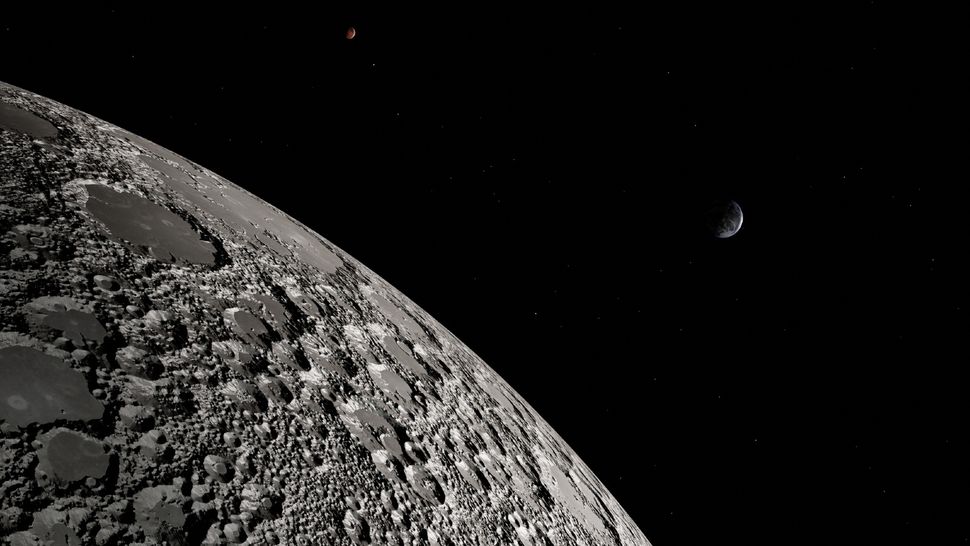
Astronauts on Mars may see a green sky, eerie new study suggests
Moon is 40 million years older than we thought, tiny crystals from Apollo mission confirm
The moon is at least 40 million years older than we once thought, a new study reveals. Scientists confirmed our cosmic companion’s new minimum age after reanalyzing tiny impact crystals from lunar samples taken by NASA’s Apollo 17 mission in 1972. Earth is approximately 4.54 billion years old. So based on the newest study, the zircon crystals were formed around 80 million years after our planet formed. However, the collision that birthed the moon could have actually happened even earlier. After the Earth-Thea crash, the infant moon’s surface would have been covered by a magma ocean due to the intense energy of the collision. Therefore, the lunar zircon crystals could only have properly solidified into their current state once the magma ocean had cooled down.
The oldest continents in the Milky Way may be 5 billion years older than Earth’s
Astrobiologists think a planet needs to have certain features to support life: oxygen in its atmosphere, something to shield organisms from dangerous radiation and liquid water, for a start. Although big land masses aren’t strictly necessary for living things to emerge, Earth’s history shows that they’re important for life to thrive and exist for long periods of time. So, if an exoplanet had continents before Earth, it follows that there might be older, more advanced life on that world.
This line of thought led Jane Greaves, an astronomer at Cardiff University astronomer in the U.K., to answer the question: When did the first continents appear on a planet in our galaxy? Turns out, two exoplanets’ continents — and perhaps life — may have arisen four to five billion years before Earth’s.
Can a Dead Star Keep Exploding?
“Because the corpse is not just sitting there, it’s active and doing things that we can detect,” Ho said. “We think these flares could be coming from one of these newly formed corpses, which gives us a way to study their properties when they’ve just been formed.”
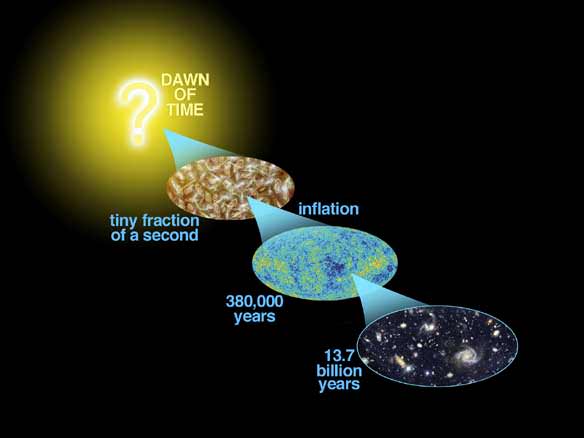
The Echoes From Inflation Could Still Be Shaking the Cosmos Today
Life Might Be Easiest to Find on Planets that Match an Earlier Earth
When methane (CH4) and oxygen (O2) are both present in an atmosphere, it’s an indication that life is at work. That’s because, in an oxygen environment, methane only lasts about 10 years. Its presence indicates disequilibrium. For it to be present, it has to be continually replenished in amounts that only life can produce.
Continue reading “The Green Skies of Mars and Other Astronomical Wonders”…








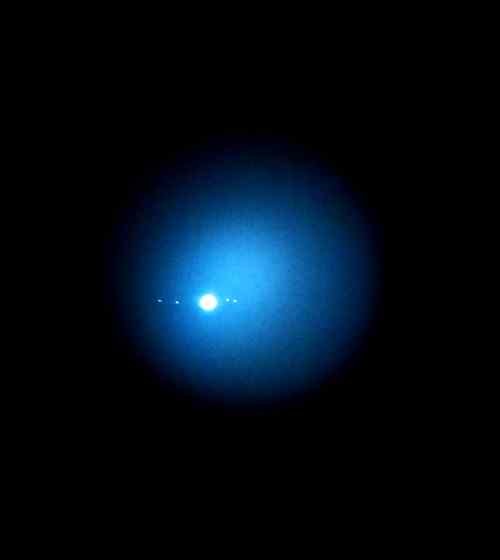
 Jupiter and Saturn, but Voyager 2 continued on to Uranus and Neptune. They’re both now outside the solar system, sending back data about the regions of space they’re exploring.
Jupiter and Saturn, but Voyager 2 continued on to Uranus and Neptune. They’re both now outside the solar system, sending back data about the regions of space they’re exploring.